Solar Battery

(Most Common Technology for Solar and large back-up application)
Lead acid battery has two electrodes one is lead (Pb) and the other is lead dioxide (PbO2) and the electrolyte here is sulfuric acid. Without getting into the detail of their chemical reaction the important thing here is there can be two major types of lead acid batteries which have different applications and frankly it can get pretty confusing since there are many many nomenclatures out there. But here is all you need to know.
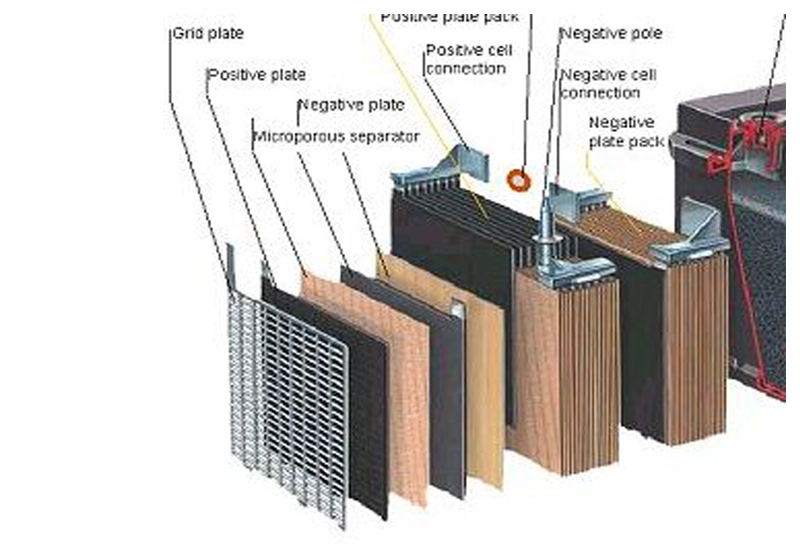
Both these batteries are lead acid batteries but the difference here lies in their making! We now know that batteries have 2 plates. One is positive and the other is negative. The difference is in the structure of these plates.
Technically speaking the positive plate of the battery is the weaker plate, so the life of the battery essentially depends on the positive plate and so the structure of positive plate is where the difference lies between the two batteries.
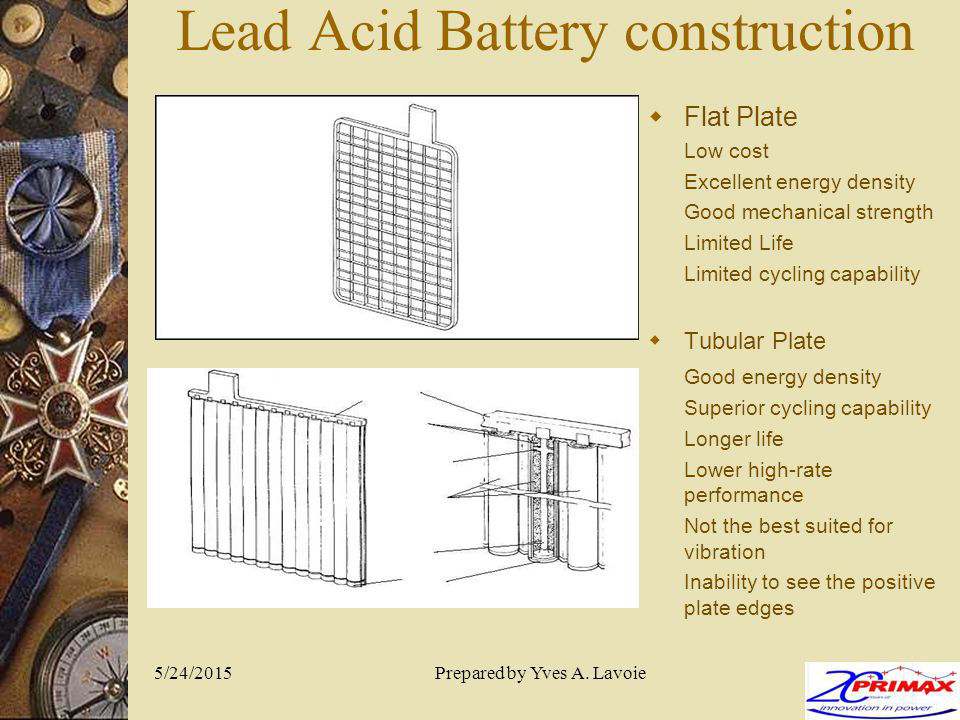
i) Flooded Lead Acid Battery : Flat Plate and Tubular plate
Flat Plate Battery : Like the name suggests in a flat plate battery both plates are essentially an ‘open flat’ plate structure, here the lead oxide material is pasted on either side of the plate
Tubular plate Battery : In Tubular batteries on the other hand the positive plate is a ‘Tube’ (made of cloth which holds the electrode inside it). The negative plate remains the same flat structure. Another major difference is that flat plate batteries have thinner plates and tubular batteries have thicker plates which are one of the major reasons why tubular batteries have larger number of discharging cycles
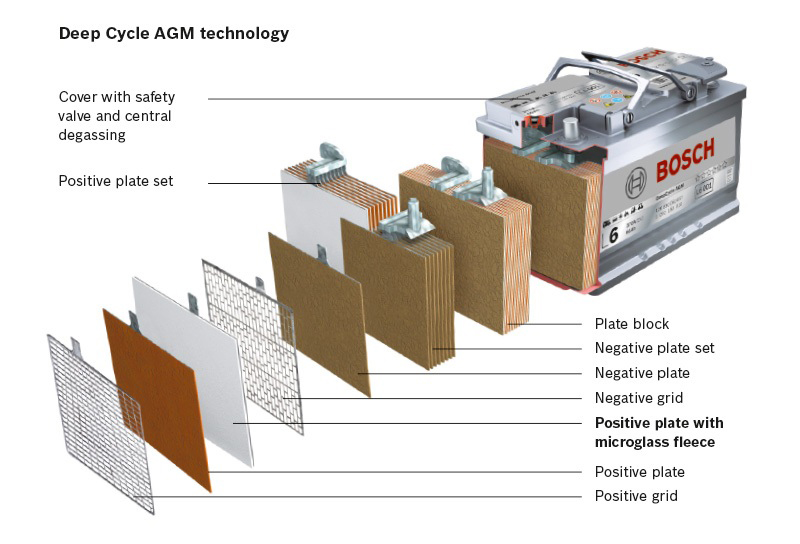
ii) Sealed Lead Acid Battery or SMF : AGM(Absorbed Glass Matt) and GEL( Gelified electrolyte)
Commonly known as Valve Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA) or Sealed Lead Acid (SLA). SLA batteries are available in a few different formats. Their principal manufacturing process, including number of plates and plate thickness determines its designated end user application. SLA batteries tend not to sulphate or degrade as easily as wet cells and are regarded the safest lead acid battery to use.
Two main versions of Sealed Lead Acid Batteries (SLA) are commonly found. AGM (Absorbed Glass Matt) and Gel Cell (gelified electrolyte).
AGM Sealed Lead Acid Battery
AGM batteries offer the best price point in the Valve Regulated Sealed lead acid variety. AGM Sealed Lead Acid Batteries utilise an Absorbed Glass Matt (AGM) process which is superior to traditional flooded technology. Fine, highly porous, micro-fiber glass separators absorb the electrolyte, increasing efficiency by lowering internal resistance, which in turn boosts capacity. Lower internal resistance also means that the battery can be recharged much faster than conventional flooded or wet lead acid batteries. AGM batteries provide much larger capacity in a smaller case size and are able to be mounted on their side and shipped using standard shipping processes.
AGM batteries are found in many applications and are commonly used in; UPS, alarm and telecommunications industries, golf carts and trundlers, mobility vehicles, performance automotive and much more. As always, it is important to ensure you are selecting the right AGM battery for your application. Although the voltage, capacity, dimensions and ratings may be very similar across a range, each AGM battery has a specific application that they should be used in.
Gel Sealed Lead Acid Types
A common misconception is that all "sealed" lead acid batteries are GEL. Gel VRLA batteries contain a gelified electrolyte which differs to their AGM counterparts. Sulfuric acid is mixed with silica fume, which makes the resulting mass gel-like and immobile. This creates a completely maintenance free, non spill able lead acid battery product. Unlike a flooded or wet-cell lead acid battery, GEL cell batteries do not need to be kept upright and can be shipped using standard shipping process'.
GEL's inherit design reduces electrolyte evaporation, spillage and subsequent corrosion issues that are very common in flooded or wet-cell batteries. GEL batteries boast greater resistance to extreme temperatures, shock, and vibration. They are capable of withstanding over discharging, which typically causes irreversible damage to Flooded and some AGM batteries. They are ideal in applications where a constant current is required such as golf carts, mobility, power bank and RV power bank applications.
GEL are generally much more expensive than their AGM and Flooded counterparts. They have a very low discharge rate (1% per month), but they require specific charging practices and need to be charged with a GEL specific battery charger.
iii) Lithium Ion battery : Usual market standard
a) lithium-iron phosphate (LiFePO4)
b)Lithium iron yttrium phosphate (LiFeYPO4).
The doping with yttrium will increase the cells life expectancy and performance. The conceptual design and chemistry of our Li-cells renders them intrinsically safe, this means in case of a problem the cells cannot catch fire. Most cell phone or laptop batteries are not intrinsically safe! Lithium cells are almost completely recyclable